This blog post demonstrates how to automate Firestore health checks using Terraform to deploy a Cloud Function (Gen 1) and set up a complete monitoring and alerting pipeline in Google Cloud.
Resources Created
This Terraform configuration will provision the following resources:
- Service Account (
google_service_account): A dedicated identity for the Cloud Function withroles/datastore.viewerandroles/cloudfunctions.invokerpermissions. - Cloud Storage Bucket (
google_storage_bucket): A bucket to store the zipped source code for the Cloud Function. - Cloud Function (
google_cloudfunctions_function): A serverless function to execute the Python health check script. - Cloud Scheduler Job (
google_cloud_scheduler_job): A cron job that triggers the Cloud Function every 5 minutes. - Log-based Metric (
google_logging_metric): A custom metric in Cloud Logging that counts log entries matching the script’s failure output. - Notification Channel (
google_monitoring_notification_channel): An email channel to send alerts to. - Alerting Policy (
google_monitoring_alert_policy): A policy in Cloud Monitoring that watches the log-based metric. If the failure count is greater than 0 for 1 minute, it sends a notification.
Prerequisites
- Terraform & Google Cloud SDK: You must have Terraform and
gcloudinstalled and authenticated. - Python Script Refactoring: The original command-line script must be adapted to work as a Cloud Function. It needs an entry point function that accepts
(event, context)arguments. Failures should be raised as exceptions rather than usingsys.exit(1). - Source Code Zip File: You must create a zip archive containing your Python script (
main.py) and arequirements.txtfile.
Example main.py Structure
Your Python code must be adapted to have a specific entry point.
# main.py
import os
import sys
from google.cloud import firestore_admin_v1
from google.api_core import exceptions
def check_firestore_health_http(event, context):
"""
HTTP-triggered Cloud Function entry point.
"""
try:
project_id = os.environ.get('GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT')
database_name = f"projects/{project_id}/databases/(default)"
client = firestore_admin_v1.FirestoreAdminClient()
request = {
"name":database_name
}
print(f"Checking status of Firestore database '{database_name}'...")
response = client.get_database(request=request)
if response.name == database_name:
print(f"Successfully connected. State UID is: {response.uid}")
return ('OK', 200)
else:
# Raise an exception to ensure the failure is logged as an error
raise RuntimeError(f"Database state is not HEALTHY.")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Health check failed: {e}", file=sys.stderr)
# Re-raising the exception ensures it's logged as an error by Cloud Functions
raise e
Example requirements.txt
google-cloud-firestore==2.21.0
Create a zip file from these two files: zip source.zip main.py requirements.txt
Terraform Example
# Terraform configuration to deploy and monitor the Firestore health check script.
# --- Provider & Variables ---
terraform {
required_providers {
google = {
source = "hashicorp/google"
version = ">= 6.0.0"
}
}
}
variable "project_id" {
description = "The Google Cloud project ID."
type = string
}
variable "region" {
description = "The Google Cloud region for deploying resources."
type = string
default = "us-central1"
}
variable "notification_email" {
description = "The email address to send monitoring alerts to."
type = string
}
variable "source_code_zip" {
description = "The path to the source code zip file for the Cloud Function."
type = string
default = "source.zip"
}
variable "function_source_bucket_name" {
description = "A unique name for the Cloud Storage bucket to store the function source code."
type = string
}
provider "google" {
project = var.project_id
region = var.region
}
# --- Enable APIs ---
# Enables the APIs required for this infrastructure.
resource "google_project_service" "apis" {
for_each = toset([
"cloudfunctions.googleapis.com", # Changed from run.googleapis.com
"cloudscheduler.googleapis.com",
"logging.googleapis.com",
"monitoring.googleapis.com",
"cloudbuild.googleapis.com", # Needed for Cloud Function deployment
])
service = each.key
disable_on_destroy = false
disable_dependent_services = true
}
# --- Service Account for Cloud Function ---
# A dedicated service account for the Cloud Function and Scheduler with necessary permissions.
resource "google_service_account" "firestore_check_sa" {
account_id = "firestore-health-check-sa"
display_name = "Firestore Health Check Service Account"
project = var.project_id
depends_on = [google_project_service.apis]
}
# Grant the 'Datastore Viewer' role to allow the script to get database status.
resource "google_project_iam_member" "datastore_viewer" {
project = var.project_id
role = "roles/datastore.viewer"
member = "serviceAccount:${google_service_account.firestore_check_sa.email}"
}
# Grant the 'Cloud Functions Invoker' role so the scheduler can trigger the function.
resource "google_project_iam_member" "function_invoker" {
project = var.project_id
role = "roles/cloudfunctions.invoker"
member = "serviceAccount:${google_service_account.firestore_check_sa.email}"
}
# --- Cloud Storage for Function Source ---
# A bucket to store the zipped source code for the Cloud Function.
resource "google_storage_bucket" "function_source_bucket" {
name = var.function_source_bucket_name
location = var.region
project = var.project_id
force_destroy = true # Set to false in production if you need to keep the bucket
}
# source.zip will contain the python script and the requirements.txt file.
resource "google_storage_bucket_object" "source_zip" {
name = "source.zip"
bucket = google_storage_bucket.function_source_bucket.name
source = var.source_code_zip
}
# --- Cloud Function (Gen 1) ---
# This function runs the Python script.
resource "google_cloudfunctions_function" "firestore_health_check_function" {
name = "firestore-health-check"
description = "Periodically checks the health of the Firestore database."
runtime = "python39" # Or your desired Python runtime
project = var.project_id
region = var.region
available_memory_mb = 128
service_account_email = google_service_account.firestore_check_sa.email
source_archive_bucket = google_storage_bucket.function_source_bucket.name
source_archive_object = google_storage_bucket_object.source_zip.name
trigger_http = true
entry_point = "check_firestore_health_http" # Must match the function name in your Python code
environment_variables = {
GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT = var.project_id
}
depends_on = [
google_project_iam_member.datastore_viewer,
google_project_iam_member.function_invoker
]
}
# --- Cloud Scheduler ---
# Triggers the Cloud Function every 5 minutes.
resource "google_cloud_scheduler_job" "run_health_check" {
name = "run-firestore-health-check"
description = "Triggers the Firestore health check Cloud Function."
schedule = "*/5 * * * *" # Every 5 minutes
time_zone = "Etc/UTC"
http_target {
uri = google_cloudfunctions_function.firestore_health_check_function.https_trigger_url
http_method = "POST"
oidc_token {
service_account_email = google_service_account.firestore_check_sa.email
audience = google_cloudfunctions_function.firestore_health_check_function.https_trigger_url
}
}
depends_on = [google_cloudfunctions_function.firestore_health_check_function]
}
# --- Log-Based Metric ---
# Creates a custom metric that counts failure logs from the health check script.
resource "google_logging_metric" "firestore_failure_metric" {
project = var.project_id
name = "firestore_health_check_failures"
description = "Counts the number of failed Firestore health checks."
filter = <<-EOT
resource.type="cloud_function"
resource.labels.function_name="${google_cloudfunctions_function.firestore_health_check_function.name}"
severity>=ERROR
textPayload=~"(^Error:|^Warning:|Permission denied|Failed to query|An unexpected error|Health check failed)"
EOT
metric_descriptor {
metric_kind = "DELTA"
value_type = "INT64"
}
depends_on = [google_project_service.apis]
}
# --- Monitoring Notification Channel ---
# Defines where to send alerts (in this case, an email address).
resource "google_monitoring_notification_channel" "email_channel" {
display_name = "Alerts Email"
type = "email"
labels = {
email_address = var.notification_email
}
}
# --- Monitoring Alert Policy ---
# Creates the alert that watches the log-based metric and triggers a notification.
resource "google_monitoring_alert_policy" "firestore_health_alert" {
project = var.project_id
display_name = "Firestore Unhealthy Alert"
combiner = "OR"
conditions {
display_name = "Firestore health check is failing"
condition_threshold {
filter = "metric.type=\"logging.googleapis.com/user/${google_logging_metric.firestore_failure_metric.name}\" AND resource.type=\"cloud_function\""
duration = "60s"
comparison = "COMPARISON_GT"
threshold_value = 0
trigger {
count = 1
}
aggregations {
alignment_period = "60s"
per_series_aligner = "ALIGN_COUNT"
}
}
}
notification_channels = [
google_monitoring_notification_channel.email_channel.id
]
documentation {
content = "The Firestore health check script is reporting failures. This indicates a potential issue with Firestore availability or the check's permissions."
mime_type = "text/markdown"
}
depends_on = [
google_logging_metric.firestore_failure_metric,
google_monitoring_notification_channel.email_channel
]
}
How to Use
-
Create a
terraform.tfvarsfile: Create a file namedterraform.tfvarsand populate it with your values:project_id = "your-gcp-project-id" region = "us-central1" notification_email = "your-alert-email@example.com" function_source_bucket_name = "unique-bucket-name-for-source-code" source_code_zip = "path/to/your/source.zip" -
Initialize Terraform:
terraform init -
Plan and Apply:
terraform plan terraform apply
Once applied, the system is fully automated. The script will run via the Cloud Function every five minutes, and you will receive an email if any failures are detected.
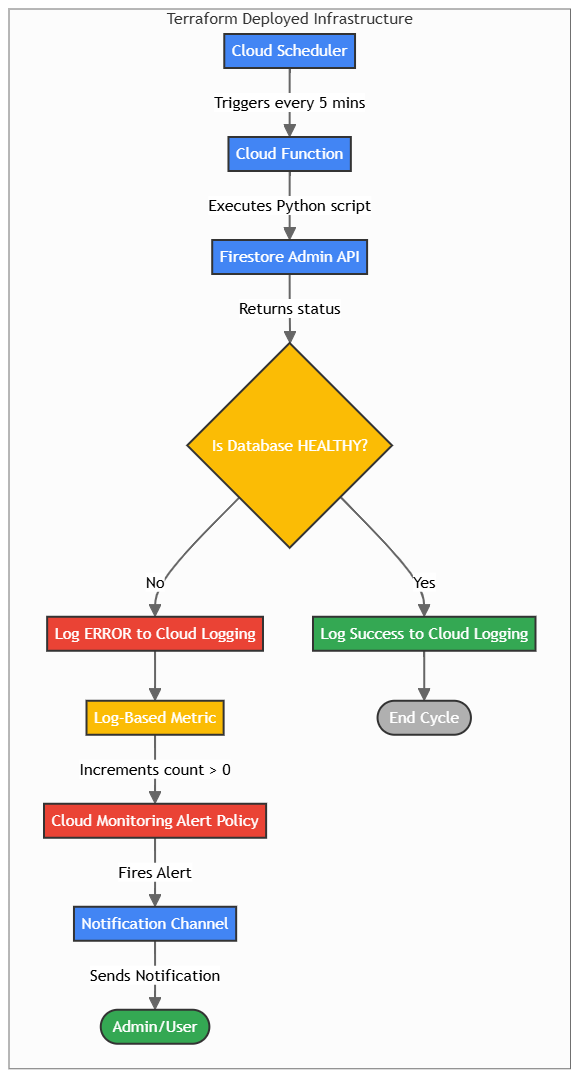
Execution Flow Diagram
This diagram illustrates how the resources provisioned by Terraform work together to monitor Firestore’s health.
graph TD
subgraph "Terraform Deployed Infrastructure"
A[<i class='fa fa-clock'></i> Cloud Scheduler] -- Triggers every 5 mins --> B[<i class='fa fa-bolt'></i> Cloud Function];
B -- Executes Python script --> C[<i class='fa fa-database'></i> Firestore Admin API];
C -- Returns status --> D{Is Database HEALTHY?};
D -- No --> F[<i class='fa fa-exclamation-triangle'></i> Log ERROR to Cloud Logging];
F --> G[<i class='fa fa-chart-bar'></i> Log-Based Metric];
G -- Increments count > 0 --> H[<i class='fa fa-bell'></i> Cloud Monitoring Alert Policy];
H -- Fires Alert --> I[<i class='fa fa-envelope'></i> Notification Channel];
D -- Yes --> E[<i class='fa fa-check-circle'></i> Log Success to Cloud Logging];
E --> L([End Cycle]);
I -- Sends Notification --> J([<i class='fa fa-user'></i> Admin/User]);
end
style A fill:#4285F4,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px,color:#fff
style B fill:#4285F4,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px,color:#fff
style C fill:#4285F4,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px,color:#fff
style D fill:#FBBC05,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px,color:#fff
style E fill:#34A853,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px,color:#fff
style F fill:#EA4335,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px,color:#fff
style G fill:#FBBC05,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px,color:#fff
style H fill:#EA4335,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px,color:#fff
style I fill:#4285F4,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px,color:#fff
style J fill:#34A853,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px,color:#fff
style L fill:#B0B0B0,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px,color:#fff
Step-by-Step Explanation:
- Cloud Scheduler (Trigger):
- Every 5 minutes, the Cloud Scheduler job sends an authenticated HTTP request to the Cloud Function’s trigger URL.
- Cloud Function (Execution):
- The HTTP request invokes the
firestore-health-checkCloud Function. - The function executes the Python script, which uses its assigned Service Account credentials.
- The HTTP request invokes the
- Firestore Admin API (Health Check):
- The Python script calls the Firestore Admin API, requesting the status of the
(default)database for the specified project.
- The Python script calls the Firestore Admin API, requesting the status of the
- Logging and Monitoring (Decision Point):
- Success Path: If the Firestore database is
HEALTHY, the function logs a success message to Cloud Logging and finishes with a200 OKstatus. No alert is triggered. - Failure Path: If the database is unhealthy, there’s a permission error, or any other exception occurs, the function logs the error message to
stderr. Cloud Logging captures this as anERRORseverity log.
- Success Path: If the Firestore database is
- Log-Based Metric (Counting Failures):
- The
firestore_health_check_failuresmetric is configured with a filter that specifically looks for theseERRORlogs from this function. - When a failure log appears, the metric’s count increases by 1.
- The
- Cloud Monitoring (Alerting):
- The “Firestore Unhealthy Alert” policy continuously watches the failure metric.
- The alert condition is triggered when the metric’s value is greater than
0for at least one minute.
- Notification Channel (Notification):
- Once the alert is triggered, Cloud Monitoring sends a notification to the configured email address, informing you of the failure.